Domain and IP settings: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tag: Manual revert |
No edit summary |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
[[Category:Configuration]] | [[Category:Configuration]] | ||
[[Category:Authentication]] | [[Category:Authentication]] | ||
[[Category:IP monitor]] | |||
<strong>How to configure domains and IPs in InboxSys</strong> | <strong>How to configure domains and IPs in InboxSys</strong> | ||
| Line 7: | Line 8: | ||
* Configure the [[domainchecker]] | * Configure the [[domainchecker]] | ||
* [[IP_monitor|Monitor IPs]] | * [[:Category:IP_monitor|Monitor IPs]] | ||
* Set an [[SNDS]] API Key | * Set an [[SNDS]] API Key | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
## Cname | ## Cname | ||
# Sender domain template | # Sender domain template | ||
## MX record | ## [[MX-Record|MX-record]] | ||
## Default [[ | ## Default [[SPF]] / [[SenderID]] record | ||
## Alternative SPF /SenderID record | ## Alternative SPF /SenderID record | ||
## Default [[ | ## Default [[DKIM]] [[DomainKeys_Identified_Mail_(DKIM)#Selector|selector]] | ||
## Default DKIM key | ## Default DKIM key | ||
## Alternative DKIM selector | ## Alternative DKIM selector | ||
| Line 51: | Line 52: | ||
=SPF / SenderID (default and alternative)= | =SPF / SenderID (default and alternative)= | ||
[[File:ip2cidr1.png|thumb|Converting an IP range starting with 1]] | |||
All IP networks that should be considered "correct" by the domainchecker when checking for SPF or SenderID can be entered in this field, separated by pipes. | All IP networks that should be considered "correct" by the domainchecker when checking for SPF or SenderID can be entered in this field, separated by pipes. | ||
| Line 60: | Line 62: | ||
Alternative SPF: 127.1.0.0/24|127.1.1.0/24|127.5.5.123/32 | Alternative SPF: 127.1.0.0/24|127.1.1.0/24|127.5.5.123/32 | ||
</pre> | |||
==Adding multiple IPs to the IP monitor== | |||
[[File:Ip2cidr2.png|thumb|Converting an IP range starting with 0]] | |||
IPs can be added individually or in correct [[CIDR]] ranges. CIDR stands for "Classless Inter-Domain Routing". | |||
* A /24 CIDR range starts from 0 in the fourth octet (class D as in A.B.C.D) and has 255 wildcard bits (Mask: 255.255.255.0). | |||
* A /32 range is a single address with 0 wildcard bits (Mask: 255.255.255.255). | |||
* The /0 range holds all IPs worldwide (that's 4.294.967.296 IPs) it starts from 0.0.0.0, ends with 255.255.255.255 and 255.255.255.255 also covers its wildcard bits (Mask: 0.0.0.0). | |||
Use [https://www.calculator.net/ip-subnet-calculator.html a subnet calculator] to calculate CIDR ranges. | |||
Example: | |||
Let's say, we want to monitor the following list of IPs: | |||
* 192.168.236.1 to 192.168.236.32 | |||
* 192.168.236.49 to 192.168.236.50 | |||
* 192.168.236.65 to 192.168.236.88 | |||
* 192.168.236.97 to 192.168.236.104 | |||
* 192.168.236.113 to 192.168.236.114 | |||
* 192.168.236.129 to 192.168.236.152 | |||
* 192.168.236.161 to 192.168.236.168 | |||
* 192.168.236.177 | |||
* 192.168.236.181 | |||
* 192.168.236.193 to 192.168.236.200 | |||
* 192.168.236.209 to 192.168.236.232 | |||
* 192.168.236.245 | |||
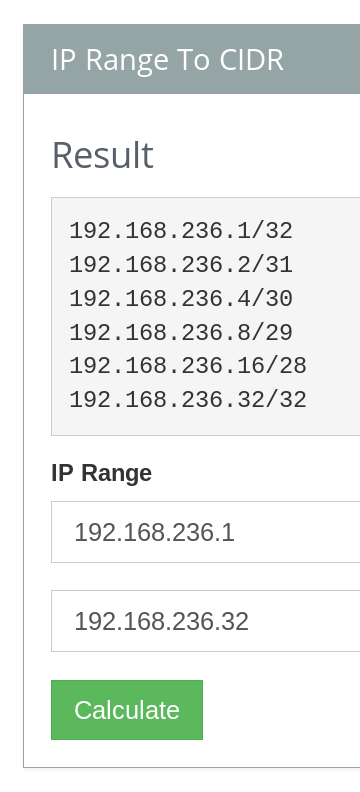
Let's start with the first line. That line contains the first 32 IPs in the /24 CIDR range, which includes 254 IPs. In fact, I found a nice website to help doing so: If you look at [https://ipaddressguide.com/cidr ipaddressguide.com], you can convert an address range to CIDR. I did this with the exact range provided. If I take the result and split the ranges with pipes, the following should be added to InboxSys: | |||
<pre> | |||
192.168.236.1/32|192.168.236.2/31|192.168.236.4/30|192.168.236.8/29|192.168.236.16/28|192.168.236.32/32 | |||
</pre> | |||
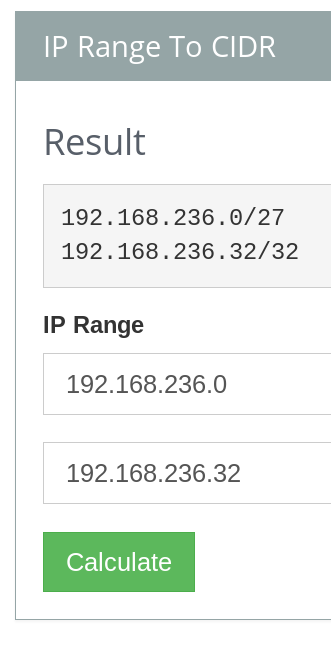
However, there is one thing to notice here. CIDR ranges typically start from 0 and not from 1. If we take in the 0, as in the second thumbnail on this page, then this is all we need to add to get the exact same result: | |||
<pre> | |||
192.168.236.0/27|192.168.236.32/32 | |||
</pre> | |||
The following example adds '''159''' IPs to the monitor, including the '''138''' IPs from the list above: | |||
<pre> | |||
192.168.236.0/27|192.168.236.32/32|192.168.236.49/32|192.168.236.50/32|192.168.236.64/27|192.168.236.96/27|192.168.236.113/32|192.168.236.114/32|192.168.236.128/27|192.168.236.161/29|192.168.236.168/32|192.168.236.177/32|192.168.236.181/32|192.168.236.192/29|192.168.236.200/32|192.168.236.208/28|192.168.236.224/29|192.168.236.232/32|192.168.236.245/32 | |||
</pre> | |||
The following example adds '''254''' IPs to the monitor, including the '''138''' IPs from the list above. It's a full /24 CIDR range: | |||
<pre> | |||
192.168.236.0/24 | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| Line 73: | Line 127: | ||
This dropdown menu shows all possible output formats for the copy/paste section in the domainchecker and other query outputs. This feature was designed to paste query results directly from InboxSys in a ticket, formatted according to the ticket system used. In case you need any format which is not in the list, or you need any other help configuring the Domain Settings, please don't hesitate to create a [https://support.inboxsys.com/login?back_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsupport.inboxsys.com%2Fissues%2Fnew support ticket]. | This dropdown menu shows all possible output formats for the copy/paste section in the domainchecker and other query outputs. This feature was designed to paste query results directly from InboxSys in a ticket, formatted according to the ticket system used. In case you need any format which is not in the list, or you need any other help configuring the Domain Settings, please don't hesitate to create a [https://support.inboxsys.com/login?back_url=https%3A%2F%2Fsupport.inboxsys.com%2Fissues%2Fnew support ticket]. | ||
=Useful links= | |||
* https://www.calculator.net/ip-subnet-calculator.html - a subnet calculator | |||
* [[wikipedia:Classless_Inter-Domain_Routing]] | |||
Latest revision as of 19:49, 7 October 2024
How to configure domains and IPs in InboxSys
"Domain settings" in InboxSys are used to:
- Configure the domainchecker
- Monitor IPs
- Set an SNDS API Key
Domain settings are found by clicking the cogwheels in the far right top, selecting "account settings" and "Domain settings". The form shown has 3 sections with the following options:
- Link domain template
- Cname
- Sender domain template
- Formatting
Template system
The dropdown menus for linkdomains and senderdomains how all link- and senderdomains that can be found in the messages in your account. Picking an option from the linkdomain template automatically changes the CNAME field to show the setting from the selected domain. Picking an option from the senderdomain template automatically changes the MX, default SPF, alternative SPF, default DKIM Key and default DKIM selector fields to show the settings from the selected domain. The alternative DKIM key and the alternative DKIM selector remain unchanged.
The template system is the way to configure all fields at once, especially when you are unsure what to set. However, it is only possible to use the template system after you have received one or more campaigns to the seedlist trigger address.
Cname
Cname's are used for link redirection. All CNAME records that should be considered "correct" by the domainchecker can be entered in this field, separated by pipes.
Example: 2 domains are used for redirection across all messages: link.example.com and image.example.com. The following lookups apply:
$ host -t cname link.example.com link.example.com is an alias for example.org. $ host -t cname image.example.com image.example.com is an alias for example.net.
In this constellation, the correct setting to put in this field is: "example.org|example.net"
MX record
All MX records that should be considered "correct" by the domainchecker can be entered in this field, separated by pipes.
SPF / SenderID (default and alternative)
All IP networks that should be considered "correct" by the domainchecker when checking for SPF or SenderID can be entered in this field, separated by pipes.
Example: Mail is primarilly sent from IPS A. Some streams go out via ISP B and rarely, Mails are being sent out from the local infrastructure. ESP A allows sending via the networks 127.0.0.0/24, 127.0.1.0/23 and 127.0.3.0/24. ESP B is allows sending via the networks 127.1.0.0/24 and 127.1.1.0/24 and the IP for the local infrastructure is 127.5.5.123. We want to set IPs fom ESP A as default and all other IPs as alternative. The correct settings are:
Default SPF: 127.0.0.0/24|127.0.1.0/23|127.0.3.0/24 Alternative SPF: 127.1.0.0/24|127.1.1.0/24|127.5.5.123/32
Adding multiple IPs to the IP monitor
IPs can be added individually or in correct CIDR ranges. CIDR stands for "Classless Inter-Domain Routing".
- A /24 CIDR range starts from 0 in the fourth octet (class D as in A.B.C.D) and has 255 wildcard bits (Mask: 255.255.255.0).
- A /32 range is a single address with 0 wildcard bits (Mask: 255.255.255.255).
- The /0 range holds all IPs worldwide (that's 4.294.967.296 IPs) it starts from 0.0.0.0, ends with 255.255.255.255 and 255.255.255.255 also covers its wildcard bits (Mask: 0.0.0.0).
Use a subnet calculator to calculate CIDR ranges.
Example:
Let's say, we want to monitor the following list of IPs:
* 192.168.236.1 to 192.168.236.32 * 192.168.236.49 to 192.168.236.50 * 192.168.236.65 to 192.168.236.88 * 192.168.236.97 to 192.168.236.104 * 192.168.236.113 to 192.168.236.114 * 192.168.236.129 to 192.168.236.152 * 192.168.236.161 to 192.168.236.168 * 192.168.236.177 * 192.168.236.181 * 192.168.236.193 to 192.168.236.200 * 192.168.236.209 to 192.168.236.232 * 192.168.236.245
Let's start with the first line. That line contains the first 32 IPs in the /24 CIDR range, which includes 254 IPs. In fact, I found a nice website to help doing so: If you look at ipaddressguide.com, you can convert an address range to CIDR. I did this with the exact range provided. If I take the result and split the ranges with pipes, the following should be added to InboxSys:
192.168.236.1/32|192.168.236.2/31|192.168.236.4/30|192.168.236.8/29|192.168.236.16/28|192.168.236.32/32
However, there is one thing to notice here. CIDR ranges typically start from 0 and not from 1. If we take in the 0, as in the second thumbnail on this page, then this is all we need to add to get the exact same result:
192.168.236.0/27|192.168.236.32/32
The following example adds 159 IPs to the monitor, including the 138 IPs from the list above:
192.168.236.0/27|192.168.236.32/32|192.168.236.49/32|192.168.236.50/32|192.168.236.64/27|192.168.236.96/27|192.168.236.113/32|192.168.236.114/32|192.168.236.128/27|192.168.236.161/29|192.168.236.168/32|192.168.236.177/32|192.168.236.181/32|192.168.236.192/29|192.168.236.200/32|192.168.236.208/28|192.168.236.224/29|192.168.236.232/32|192.168.236.245/32
The following example adds 254 IPs to the monitor, including the 138 IPs from the list above. It's a full /24 CIDR range:
192.168.236.0/24
DKIM selector (default and alternative)
Each DKIM selector field can hold one selector. This way, it is possible to add max. 2 selectors, for the domainchecker to consider "correct" on your domains.
DKIM key (default and alternative)
Each DKIM key field can hold one DKIM key. This way, it is possible to add max. 2 public keys, for the domainchecker to consider "correct" when checking DKIM settings on your domains.
Formatting
This dropdown menu shows all possible output formats for the copy/paste section in the domainchecker and other query outputs. This feature was designed to paste query results directly from InboxSys in a ticket, formatted according to the ticket system used. In case you need any format which is not in the list, or you need any other help configuring the Domain Settings, please don't hesitate to create a support ticket.
Useful links
- https://www.calculator.net/ip-subnet-calculator.html - a subnet calculator
- wikipedia:Classless_Inter-Domain_Routing